Introduction
Blockchain technology has gained immense popularity due to its potential to revolutionize various industries. However, one of the major challenges faced by blockchain networks is scalability. In this article, we will delve into the concept of blockchain scalability, explore the blockchain scalability trilemma, and discuss some of the popular blockchain scaling projects.
What is Blockchain Scalability?
Blockchain scalability refers to the ability of a blockchain network to handle an increasing number of transactions and users without compromising its performance. Traditional blockchain networks, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, face scalability issues as their transaction processing speeds are relatively slow compared to traditional payment systems. This limitation restricts their use in real-world applications where high transaction speeds are essential.
The Blockchain Scalability Trilemma
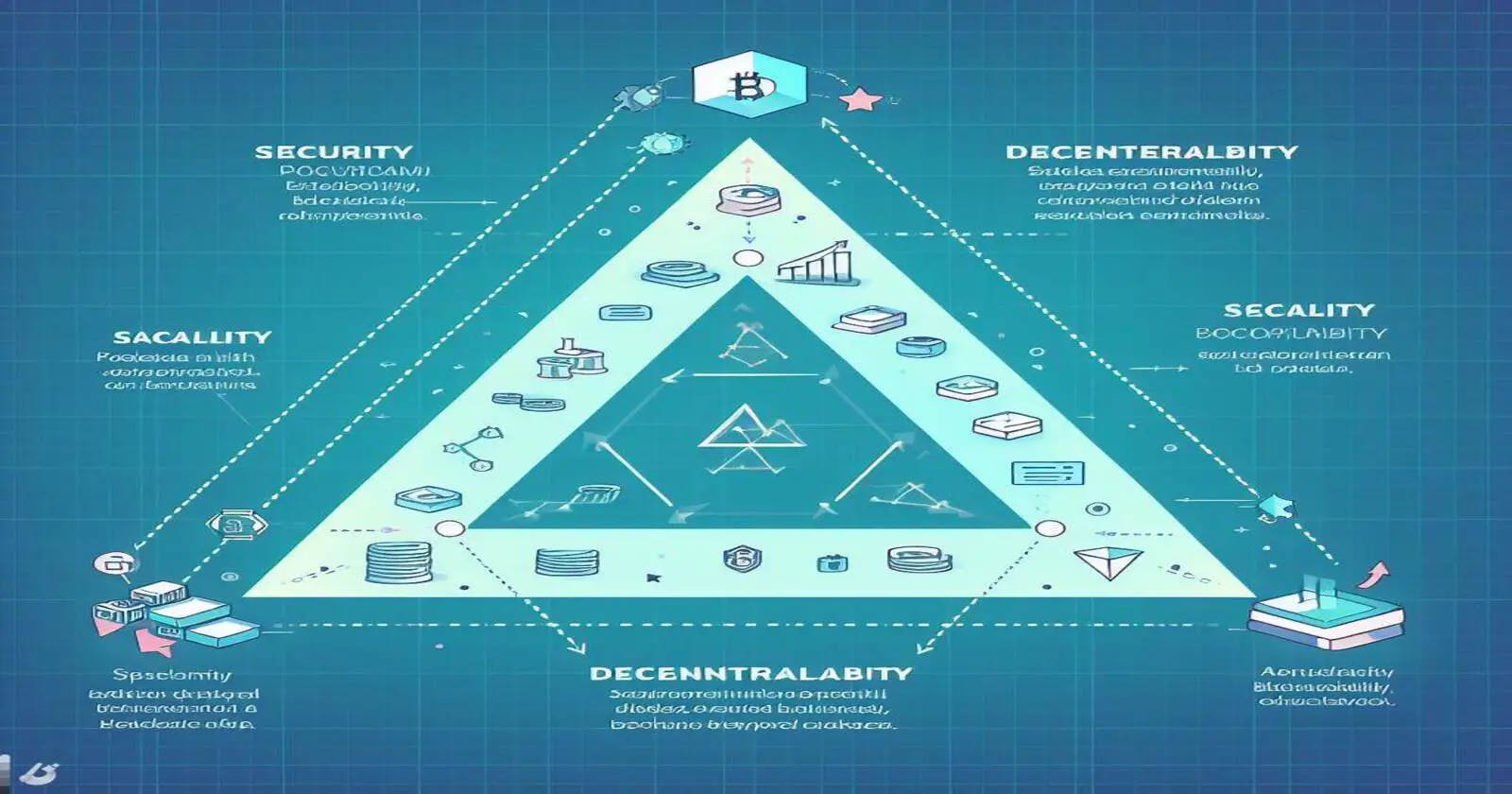
The blockchain scalability trilemma, coined by Vitalik Buterin, refers to the trade-off between decentralization, security, and scalability in blockchain networks. According to this trilemma, it is challenging to achieve all three properties simultaneously. Let's explore each aspect in detail:
Decentralization: Decentralization is a fundamental characteristic of blockchain networks, ensuring that no central authority has control over the network. It allows for trust minimization and prevents censorship. However, achieving high levels of decentralization often leads to scalability limitations.
Security: Security is crucial in blockchain networks to prevent malicious activities like double-spending and 51% attacks. Higher levels of security are often achieved through decentralization, but it can come at the cost of scalability.
Scalability: Scalability refers to the ability of a blockchain network to handle a large number of transactions quickly. Improving scalability without compromising decentralization and security is a significant challenge in the blockchain space.
Blockchain Scalability Problems
The scalability issues in blockchain networks arise due to several factors:
Transaction Speed: Traditional blockchain networks, like Bitcoin, have limited transaction processing speeds. Bitcoin, for example, can only process a few transactions per second, which is significantly slower than traditional payment systems.
Network Congestion: As more users join a blockchain network, the network can become congested, leading to delays in transaction confirmations. The limited block size and block generation times contribute to this congestion.
Increased Storage Requirements: As the blockchain grows, the storage requirements for full nodes increase. This can lead to slower synchronization times and make it difficult for new nodes to join the network.
Solutions for Blockchain Scalability
To address the scalability challenges, various solutions and approaches have been proposed in the blockchain space. Let's explore some of the popular blockchain scalability solutions:
Off-chain Solutions
Off-chain solutions, also known as second-layer scalability solutions, aim to alleviate the scalability issues by moving certain transactions off the main blockchain. These solutions include payment channels and sidechains.
Payment Channels: Payment channels allow users to conduct transactions off the main blockchain, reducing the need for on-chain transactions. It enables fast, low-cost transactions between two parties. The Lightning Network for Bitcoin and the Raiden Network for Ethereum are examples of payment channel implementations.
Sidechains: Sidechains are separate blockchains connected to the main blockchain, allowing for the offloading of certain applications and transactions. Sidechains can enhance scalability by reducing the load on the mainchain. Projects like Plasma and Parachain utilize sidechain technology to achieve scalability.
Sharding
Sharding is a technique that involves dividing the blockchain network into smaller, more manageable parts called shards. Each shard can process its transactions and maintain its state, allowing for parallel processing and increased throughput. Sharding enables blockchain networks to handle a higher volume of transactions and achieve scalability. Ethereum 2.0 is implementing sharding to address its scalability challenges.
Protocol Upgrades
Protocol upgrades, such as Segregated Witness (SegWit) and Optimistic Rollups, aim to improve blockchain scalability by optimizing the underlying protocols.
SegWit: SegWit is a protocol upgrade for Bitcoin that improves transaction efficiency and capacity. It separates the witness data from the transaction data, allowing for more transactions to fit into a block.
Optimistic Rollups: Optimistic Rollups are a layer 2 scaling solution that moves most transaction processing off-chain while still ensuring the security of the main blockchain. It allows for faster and cheaper transactions by aggregating multiple transactions into a single proof.
Consensus Algorithm Improvements
Consensus algorithm improvements can also contribute to blockchain scalability. For example, the transition from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanisms can significantly improve scalability by reducing the computational requirements for block validation. Ethereum is undergoing a transition to PoS with the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade.
Popular Blockchain Scaling Projects
Several blockchain scaling projects have gained prominence in the industry. Let's take a look at some of them:
Bitcoin Lightning Network: The Lightning Network is a second-layer scaling solution for the Bitcoin blockchain. It enables fast and cheap transactions by creating payment channels between users.
Ethereum 2.0: Ethereum 2.0 is a major upgrade that aims to improve scalability by implementing sharding and transitioning to a PoS consensus mechanism.
Polkadot: Polkadot is a multi-chain platform that enables the interoperability of different blockchains. It utilizes a scalable and secure sharding approach to achieve blockchain scalability.
Cardano: Cardano is a blockchain platform that aims to provide scalability through its unique PoS consensus algorithm called Ouroboros.
Binance Smart Chain: Binance Smart Chain is a parallel blockchain to the Binance Chain that aims to provide high performance and low fees for decentralized applications.
Conclusion
Blockchain scalability is a crucial aspect for the widespread adoption of blockchain technology. While the blockchain scalability trilemma poses a challenge, various solutions and projects are actively working towards improving scalability without compromising decentralization and security. Off-chain solutions, sharding, protocol upgrades, and consensus algorithm improvements are some of the approaches being explored. As the blockchain space continues to evolve, scalability will remain a key focus area to unlock the full potential of blockchain technology.
Additional Information: Blockchain scalability is a complex and ongoing research area, with new solutions and projects emerging regularly. It is important for blockchain networks to strike a balance between scalability, decentralization, and security to ensure the long-term success and adoption of the technology.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as financial or investment advice. Always do your own research and consult with a professional before making any investment decisions.